Wiring hardness
The electrical circuits of the Jeep MB, Ford GPW, and Hotchkiss M201 are much more than simple wires and components. They are the brain of these iconic off-road vehicles, ensuring their proper functioning and connectivity. In this article, we will explain the differences between the original 6 volts models, the modifications to 12 volts, and the configurations in 24 volts.
Additionally, we will explore the evolution of wiring harnesses over the years, considering various models and added elements over time. Get ready for an electrifying exploration of the history of Jeeps !
1. The 6 volts electrical circuit
The Jeep Willys MB and Ford GPW were equipped with original 6 volts electrical circuits, like all vehicles of that era before the general shift to 12 volts in the mid-1960s.
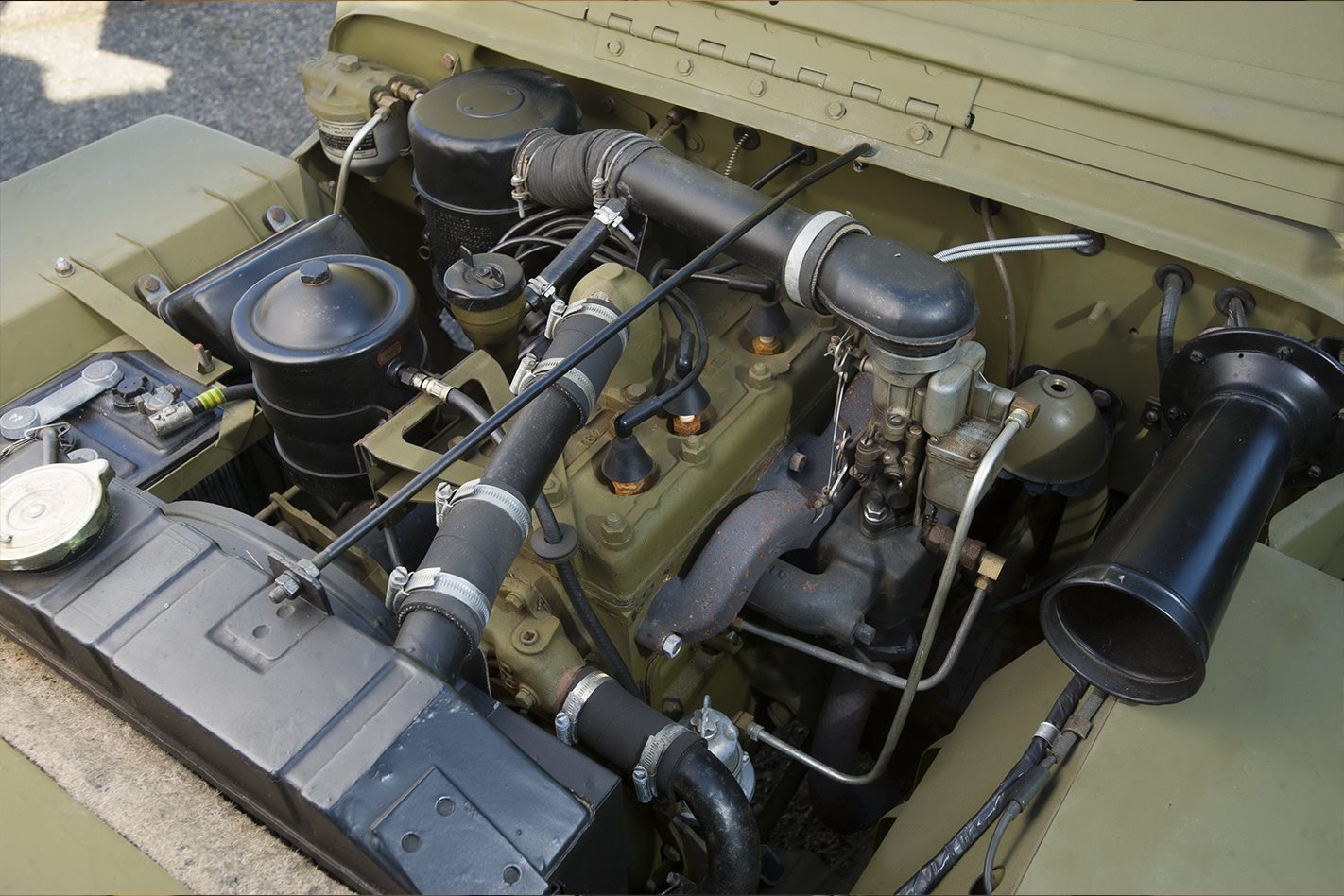

Original 6-volt assembly of L4-134 Go-Devil engine in a Willys MB
The advantage of the 6 volts system is mainly for the vehicle's history, allowing you to retain all original parts. However, switching to 12 volts provides better voltage, avoiding excessive power loss due to connections.
Losing 1 volt in a 6 volts system results in a power loss of 30% ! A decrease in voltage, even by 0.1 here and 0.4 there with lights, blackouts, sirens, etc., adds up quickly. Reduced voltage means decreased intensity in your lights and starting difficulties, hence the well-known flickering of lights in our older vehicles when starting. Many argue that a well-prepared 6 volts system is as reliable as a 12 volts system !
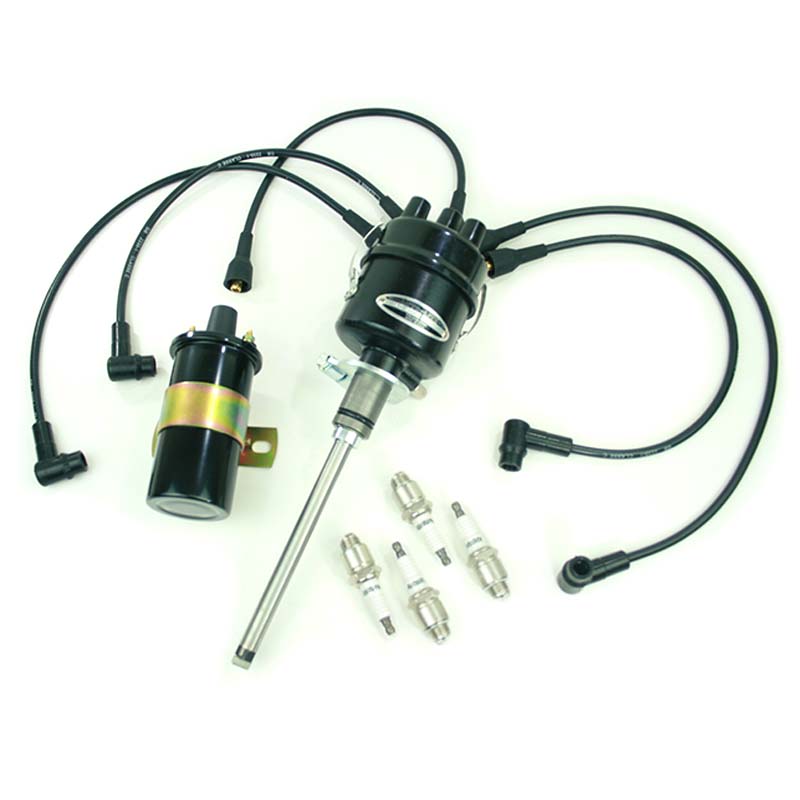
1. Complete 6 volts ignition kit (WOA9075K6V) 2. 6 volts Starter (WOA1245) 3. 6V 145AH Battery (WOA1238)
2. Modifications to 12 volts
To meet changing owner needs, many Jeeps were modified to operate on 12 volts. This reasoning was present even during WWII, for example, the 1942 Ford GPA which is originally 12 volts, or the radio Jeeps like the MZ Radio used by the U.S.M.C. with its 2 6 volts batteries behind the seats and a 12 volts "Power Take-Off" generator between the seats for the SCR-193-K radio.


Willys MB "MZ Radio" of the U.S. Marine Corps with its "Power Take-Off" and 2 6V batteries
The numerous advantages of switching to 12 volts include limiting voltage losses due to connections, part availability, and lower replacement costs. The conversion involves replacing several components:
- Battery
- Regulator (modern cards allow choosing 6V/12V)
- Starter
- Coil
- Horn
- All bulbs
- Also, the flasher unit, siren, and windshield wiper motors if present
The gauges do not necessarily need to be changed; very often, the transmitter and gauges function well during the transition from 6 volts to 12 volts.
Regarding the dynamo, it doesn't need to be replaced either, as it will adapt to the regulator to operate with your 12 volts system.
Another solution, though it may raise some eyebrows, is to replace both the regulator and the dynamo with an alternator, which is lighter and less bulky.
Another modern solution to enhance the reliability of your Jeep is to opt for an electronic ignition instead of points and condenser, which are consumables. In addition to preserving your original distributor, this electronic ignition improves your starting performance without altering the character of your Jeep.
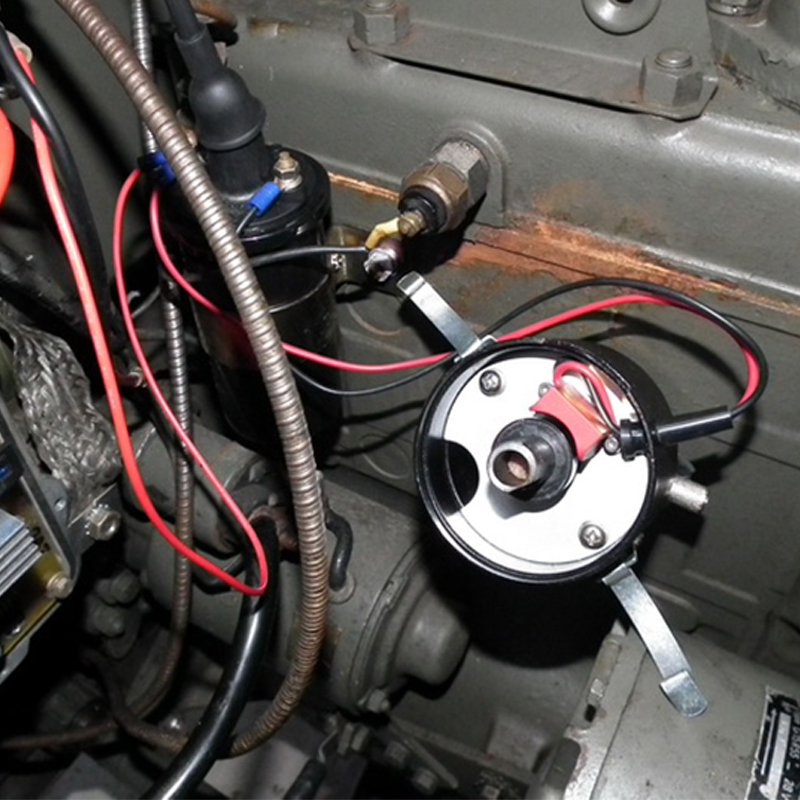
Electronic ignition in 12 volts within the distributor, replacing points and condenser
This kit installs in the AUTO-LITE, DUCELLIER, or PRESTOLITE distributor, replacing the points and condenser. Installation on your Jeep requires no modification to the distributor or drilling. Connect the black wire to the - and the red wire to the + of the coil.
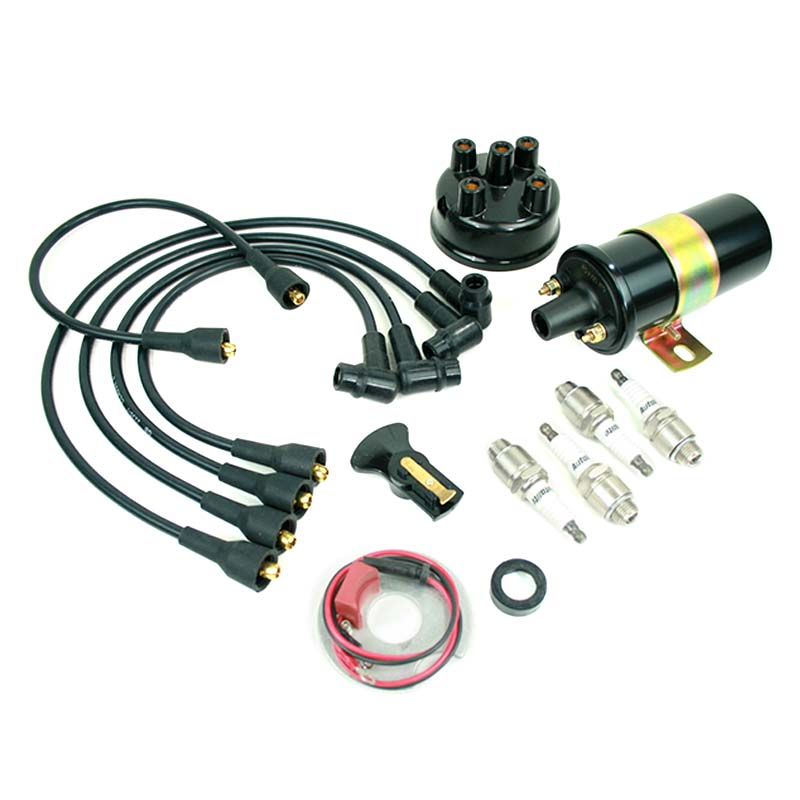
1. 12V Conversion Kit (WOA1662K) 2. 6V/12V Regulator (WOA1409E) 3. 12V 60AH Battery (WO800699)
3. The 24 volts Electrical System
The French army made its mark on the electrical systems of Hotchkiss M201 by adopting a 24 volts system instead of the 6 volts system starting from 1960.
This modification allowed for the installation of the 24 volts NATO radio pre-equipment with interference suppression, opting for armored ignition to provide better electronic protection during fording.



Hotchkiss M201 with its 24-volt electrical system and armored ignition (photos: Dallas Auto Parts)
In addition to the simple reason of military uniformity (most land/sea/air vehicles were in 24 volts), the 24-volt electrical system with armored ignition is more reliable and robust in war conditions with radios compared to the 6 volts of the early Hotchkiss M201 (with still American parts from World War II).
While there are many advantages for the military, today, 24-volt Hotchkiss M201 with armored ignition has disadvantages in civilian use, notably the cost and rarity of spare parts, as it is more complex, more expensive to manufacture, and uniquely French.
For comparison, standard spark plug wires are around €50, while armored spark plug wires are around €300, the same goes for the four spark plugs, which increase from €20 to €100.
For this reason, we offer a non-armored 24-volt ignition kit as a replacement for the complete ABG Paris distributor, spark plug wires, and spark plugs.
1. Armored 24V ignition kit (ABG63435K) 2. Non-armored 24V ignition kit (WOA9075K24V) 3. 12V 45AH Battery (HO81080P) x2
4. Evolution of Wiring Harnesses
Jeeps have seen their wiring harnesses evolve over the years, incorporating elements such as the toggle lighting switch becoming rotary, the trailer socket, and the blackout drive. Here is an image illustrating which wiring harness corresponds to your Willys MB or Ford GPW.
For your information:
- The toggle lighting switch is present until late 1943.
- The rotary lighting switch is present until 1945 but also on the M201.
- The filterette is always accompanied by ground braids on the vehicle, and the "S" on the hood.
- There was no trailer socket until serial number 200678 (January 1943).
- There was no Black-Out Drive on the Willys MB until serial number 163749 (August 1942).

WOA2000A - WOA2000AD - WOA2000B - WOA2000BD - WOA2000C - WOA2000CD
P.S: We recommend the WOA2000CD harness for adapting to your Hotchkiss M201.
5. Supports, Braids, and Wiring
Finally, let's look at what surrounds the electrical circuit, starting with the ground braids as mentioned earlier.
The interference suppression system for the radio primarily consists of "Bond Straps" and "Fastenings," which are the set of 18-piece ground braids (pre-model number 289001) and 8 pieces subsequently. As mentioned above, the filterette under the passenger-side dashboard also helps eliminate (or at least minimize) electrical system interference on radio transmissions and makes the vehicle harder to locate.

Connection of the filterette in the electrical circuit: cable to the primary side of the coil, cable to the battery, cable to the regulator (B), cable to the ammeter, cable to the ignition switch.
Interference suppression aims to eliminate interference at the source (spark plugs, switch, generator, etc.) by using resistors and capacitors or containing them in a limited space by making the engine compartment a closed cage using ground cables and new grounds made with toothed fan washers under each attachment.
A Jeep fully equipped with the interference suppression system bears an "S" letter next to the registration number on the hood.

Willys MB equipped with the interference suppression system, at least in front, with the presence of the "S."
For the installation of your harness, we recommend doing it previously on the body before it is installed on your chassis. You will also need the grommet kit (rubber and later felt after the rubber shortage in 1943) as well as the harness fixing collar kit for Willys MB or Ford GPW.
Electrical Diagram (6 volts)
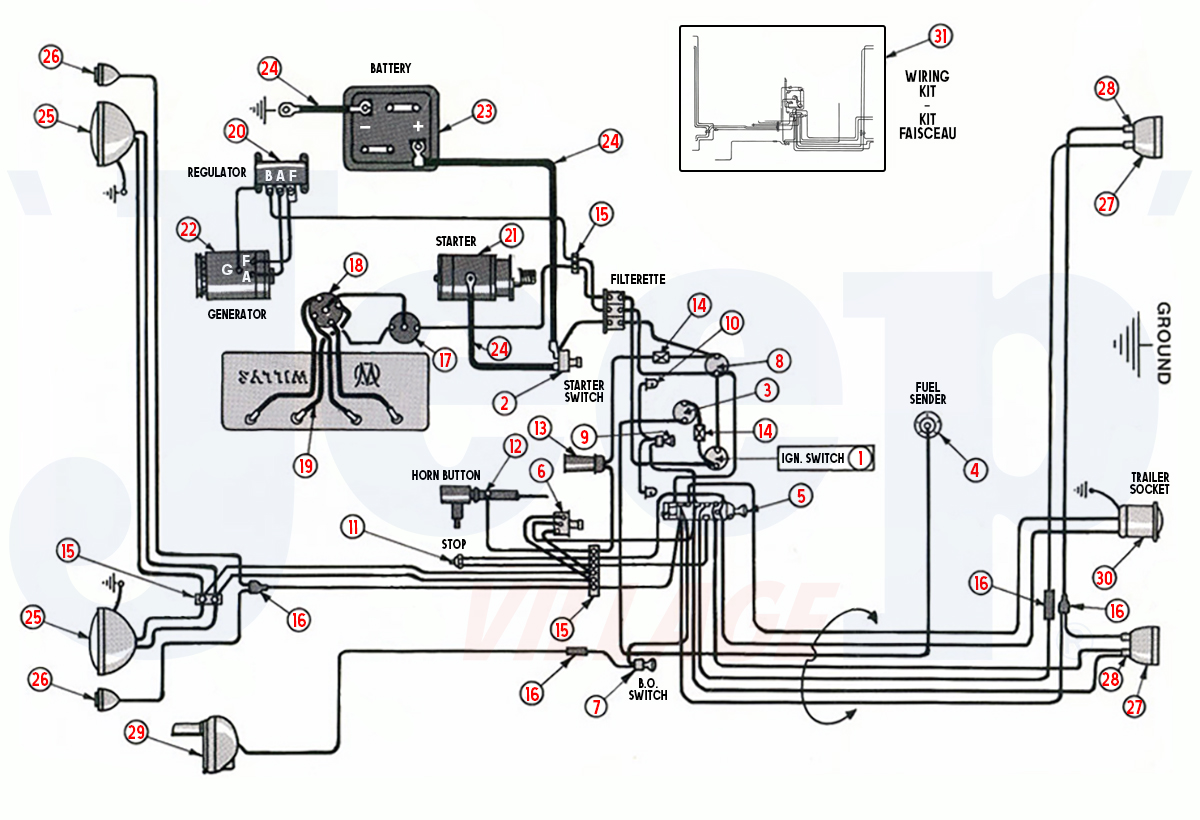
Click on the number to access the products:
1. Ignition switch 2. Foot starter switch 3. Fuel gauge 4. Fuel transmitter 5. Lighting switch 6. Headlight dimmer switch 7. B.O Drive switch 8. Ammeter gauge 9. Panel lights switch 10. Dashboard lighting
11. Stop switch 12. Horn button 13. Sparton horn 14. Circuit breaker 15. Terminal block 16. Wire connector 17. Ignition coil 18. Distributor 19. Spark plugs & wires 20. Regulator
21. Starter 22. Dynamo 23. Battery 24. Battery cable 25. Front light 26. Grille blackout light 27. Rear blackout light 28. Rear blackout light wire 29. Fender blackout light 30. Trailer socket 31. Wiring harness
In Conclusion
The electrical circuit is the neural network of Willys MB, Ford GPW, and Hotchkiss M201, contributing to their efficiency and legendary performance. By exploring the history and evolution of these systems, as well as the possibilities for modification and improvement, Jeepers can not only preserve the authenticity of their Jeeps but also adapt them to their needs in 6 volts, 12 volts, and 24 volts.




















